bFGF-grafted electrospun fibrous scaffolds via poly(dopamine) for skin wound healing
Abstract
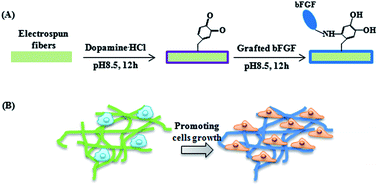
Electrospun fibrous membranes coated with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) are effective medical devices to promote wound healing. However, the current strategies of adding bFGF generally cause degradation of electrospun materials or damage to the bioactivity of the biomolecules. Here, we have developed a simple strategy for surface bFGF-functionalization of electrospun fibers in an aqueous solution, which maintained original fiber properties and growth factor bioactivity. Polydopamine (PDA) forming the mussel foot protein was chosen as an adhesive polymeric bridge-layer between substrate poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) fibers and bFGF. The bFGF-grafted PDA was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy, water contact angle measurements, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Improved hydrophilicity together with a stable fibrous structure and biodegradable fibrous matrix suggested that the PLGA/PDA-bFGF electrospun fibrous scaffolds have great potential for promoting wound healing. In vitro experiments showed that the bFGF-grafted PLGA electrospun fibrous scaffolds have highly enhanced adhesion, viability, and proliferation of human dermal fibroblasts. In vivo results showed that such scaffolds shortened wound healing time, accelerated epithelialization and promoted skin remodeling. Therefore, this PDA modification method can be a useful tool to graft biomolecules onto polymeric electrospun fibrous scaffolds which are potential scaffold candidates for repairing skin tissue.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...