Photonic crystal coupled porous BiVO4 hybrid for efficient photocatalysis under visible light irradiation
Abstract
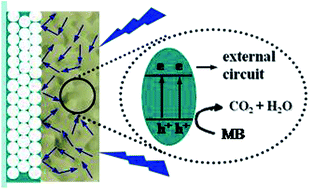
A bilayer TiO2 photonic crystal (PC)/porous BiVO4 was constructed by using liquid-phase deposition (LPD) and spin coating method for the enhancement of visible-light-driven photocatalytic ability by the improvement of light absorbance. Crystal form, morphology, film thickness, and light absorption performance were investigated. The photocatalytic activity of the bilayer TiO2 PC/porous BiVO4 film was evaluated by the degradation of MB and was compared with that of porous BiVO4 film. The effect of the film thickness of the porous BiVO4 on its photocatalytic ability was determined. It was found that the film thickness significantly affected the light absorption, and therefore its photocatalytic ability. The bilayer film with 1.03 μm of thickness of porous BiVO4 film exhibited the highest photocatalytic performance. The photocatalytic ability of porous BiVO4 was enhanced by combination with a TiO2 PC layer as the back reflector. This increase could be attributed to the intensified light absorbance produced by reflection from the TiO2 PC layer. The effects of porous structure and the application of photoelectrocatalytic process on the photocatalytic performance were also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...