Morphology analysis of near IR sensitized polymer/fullerene organic solar cells by implementing low bandgap heteroanalogue C-/Si-PCPDTBT†
Abstract
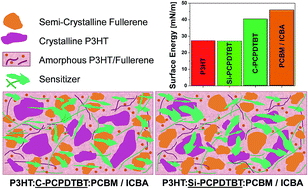
In the current work, we have investigated the morphological aspects of the ternary solar cells based on host matrices of P3HT:PCBM and P3HT:ICBA, using the low bandgap polymer analogues of C- and Si-bridged PCPDTBT as near IR sensitizers, which show noticeably different performance. A direct comparison of these well-functional and poorly functional ternary blend systems provides insights into the bottlenecks of device performance and enables us to set up an initial set of design rules for ternary organic solar cells. Our study reveals the importance of surface energy as a driving force controlling sensitizer location and morphology formation of ternary blends. The interfacial surface energy results indicate that Si-PCPDTBT locates at amorphous interfaces and P3HT crystallites, while C-PCPDTBT tends to accumulate at amorphous interfaces and semi-crystalline (or agglomerated) domains of the fullerene derivatives. GIWAXS and SCLC results support this prediction where adding high content of C-PCPDTBT influences mainly the semi-crystallinity (aggregation) of the fullerene and reduces the electron mobility, but Si-PCPDTBT impacts mainly the P3HT ordering and, in turn, deteriorates the hole mobility. These findings show that the disruption of the fullerene semi-crystalline domains is more detrimental to the device performance than the disruption of the polymer domains.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...