Gold nanoparticles embedded in Ta2O5/Ta3N5 as active visible-light plasmonic photocatalysts for solar hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
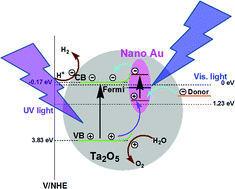
Here, we demonstrate a new recreating photocatalytic activity of a Nano Au/Ta2O5 composite for hydrogen evolution from water as a visible-light-responsive plasmonic photocatalyst by embedding Au nanoparticles in a Ta2O5 host lattice. The Nano Au/Ta2O5 composite samples were prepared through a simple Pechini-type sol–gel process. Further nitridating Nano Au/Ta2O5 composite samples in ammonia flow at 1123 K yielded Nano Au/Ta3N5 composite samples. The obtained Nano Au/Ta3N5 composite exhibited a significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity in the visible region for hydrogen evolution from water compared with blank Ta3N5 nanoparticles. UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectra and photocatalytic activity measurements indicated that the excitation of surface plasmon resonance of Au nanoparticles is responsible for the new recreating photocatalytic activity of the Nano Au/Ta2O5 composite and significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity of the Nano Au/Ta3N5 composite for hydrogen evolution in the visible region, which might be ascribed to the charge transfer effect in Nano Au/Ta2O5 composite and the synergetic effect of charge transfer and near-field electromagnetic effect in Nano Au/Ta3N5 composite induced by surface plasmon resonance of embedded Au nanoparticles. The current study could provide a new paradigm for designing plasmonic metal/semiconductor composite systems for photocatalytic, photovoltaic and other optoelectronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...