Gel electrolyte materials formed from a series of novel low molecular mass organogelators for stable quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
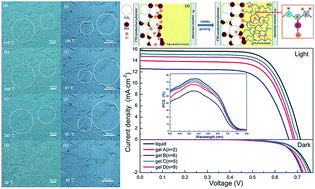
Electrolyte materials are the key components in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) and are very crucial to the performance and long-term stability of DSCs. We developed a series of diamide derivatives as novel low molecular mass organogelators (LMOGs) for DSCs. These LMOGs contain different numbers (2, 6, 5 and 9) of methylene groups (–CH2–) between the two amide carbonyl groups and exhibit distinctive self-assembly behaviors. The gel electrolytes prepared by these LMOGs possess high gel-to-solution transition temperatures (over 100 °C) and the stability of DSCs is largely enhanced. More importantly, the parity of the number of –CH2– and their special molecular arrangements have a remarkable influence on the self-assembly of the gelators resulting in a significantly different morphology, and further influence the photovoltaic performances of DSCs. It is found that the LMOGs containing odd-numbered –CH2– lead to a much better charge transport of the gel electrolytes, inducing a longer electron lifetime and higher incident photon-to-electron conversion efficiency compared with the LMOGs containing even-numbered –CH2–. Finally, a superior quasi-solid-state DSC based on the gelator containing five –CH2– is obtained, which exhibits a photoelectric conversion efficiency of 7.53% and excellent thermal and light-soaking stabilities during accelerated aging tests.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...