Monodispersed hollow platinum nanospheres: facile synthesis and their enhanced electrocatalysis for methanol oxidation
Abstract
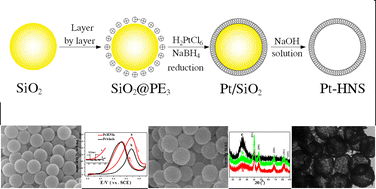
Hollow metallic nanospheres with specific composition in different sizes and shapes have drawn enormous interest due to their strong catalytic activity. In this work, we present an efficient method for facile synthesis of monodispersed Pt hollow nanospheres (Pt-HNSs) using colloidal silica nanoparticles as a sacrificial template. Two steps were involved in the fabrication process. At first, a uniform durable thin layer of anionic PtCl62− was grown on a solid surface of freshly-made polyelectrolyte-modified nano-silica, which has evenly-spread positive charges in the outmost surface, as a result of the sequential adsorption in the order of cationic PDDA [poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)], anionic PSS [poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)] and PDDA through electrostatic interaction by a layer by layer (LBL) self assembly. Then, the PtCl62− species were chemically reduced by NaBH4 in the presence of trisodium citrate dehydrate as a complex agent, followed by the chemically removing of the template. The composition, structural morphology and electrocatalytical properties of the as-prepared Pt-HNSs were thoroughly characterized by techniques, such as high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and cyclic voltammetry (CV). The results show that the as-prepared well-dispersed Pt-HNSs with narrow size distribution, exhibit significant catalytic activity to the oxidation of methanol, when compared with that of commercial Pt-black.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...