Manipulating the horizontal morphology and vertical distribution of the active layer in BHJ-PSC with a multi-functional solid organic additive†
Abstract
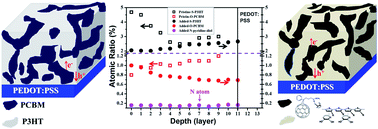
A new type of simple organic solid additive, 2,3-pyridinediol, was added into the active layer of a Bulk Hetero-Junction Polymer Solar Cell (BHJ-PSC) to improve the processing and power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the device. The 2,3-pyridinediol additive, which has pyridyl and hydroxyl groups, can interact with both P3HT and PC61BM (via π–π interactions or/and hydrogen-bonding), reorganizing the phase/domain and vertical distribution of the blended film. Therefore, even without thermal annealing, P3HT/PC61BM/2,3-pyridinediol film forms bicontinuous interpenetrated nano-domain networks with more P3HT close to the PEDOT:PSS anode. The 2,3-pyridinediol additive also can improve the efficiency of BHJ-PSCs based on other n-type materials such as ICBA (PCE of the device based on ICBA/P3HT increased from 3.35 to 5.93% after addition of the additive) and p-type materials such as PTB7 (PCE of the device using a PTB7/PC71BM active layer increased from 5.30 to 7.54% after addition of the additive). Moreover, the thermal stability of the PTB7/PC71BM/2,3-pyridinediol blended film is better than PTB7/PC71BM blended with 1,8-diiodooctane. When the active films were heated at 100 °C for 30 min, the PCE of PSC based on PTB7/PC71BM/1,8-diiodooctane decreased 20% (from 6.62% to 4.26%), whereas the PCE of PSC using a PTB7/PC71BM/2,3-pyridinediol blended film as an active layer decreased only ca. 3% (7.54% decreased to 7.30%). A small molecule solid additive in the active layer can mix well with the active components and will not be removed during the device fabrication processes. Therefore, the morphology of the active film can be well-controlled and PCEs of the corresponding devices are more reproducible.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...