Enlarging the d-spacing of graphite and polarizing its surface charge for driving lithium ions fast†
Abstract
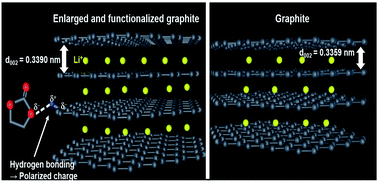
Lithium ion transport was accelerated within graphite by controlling its d-spacing as well as its functional groups. By oxidizing bare graphite under a mild condition, expanded graphites (EG* where * = functional groups) were obtained with increasing d-spacing from 0.3359 nm to 0.3395 nm as well as with functional groups formed on the plane or at the edges of graphites. The subsequent thermal reduction of EG* led to an insignificant change of d-spacing (0.3390 nm), simultaneously eliminating a portion of the functional groups (EG). The enlargement of d-spacing reduced kinetic hindrance of lithium ion movement within the expanded graphites (EG* and EG) by reserving more space for the ionic transport route. In addition, the activation energy of lithium ion intercalation in EG* was reduced by surface charge polarization of graphites induced by hydrogen bonds between oxygen atoms of carbonates in electrolytes and hydrogen atoms of surface functional groups of the expanded graphites, even if the degree of graphitization decreased. Re-graphitization induced by the subsequent thermal reduction increased delithiation capacities (QdLi) of EG as an anode for lithium ion batteries especially at high currents: QdLi at 50 C = 243 mA h g−1 for EG versus 66 mA h g−1 for bare graphite.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...