Correlation of the electronic structure of an interconnection unit with the device performance of tandem organic solar cells†
Abstract
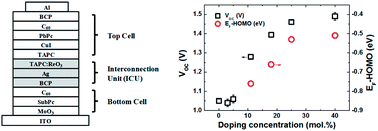
We report the correlation of the electrical properties of the p-doped layer in an interconnection unit with the performance of tandem organic photovoltaic (TOPV) cells where the interconnection unit (ICU) is composed of an electron-transporting layer (ETL)/metal/p-doped hole-transporting layer (p-HTL) by systematically varying the doping concentration of the p-HTL in the ICU. The open circuit voltage is significantly increased as the doping concentration of the p-HTL increases due to the reduction of the difference between the Fermi level and the highest occupied molecular orbital level of the p-HTL. The fill factor is also enhanced with increases in the doping concentration of the p-HTL due to the enhancement of the conductivity in the p-HTL and efficient hole transport at the interface between Ag and the p-HTL through the tunneling process, rather than through the thermionic process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...