Ionic liquid electrolytes for high-voltage rechargeable Li/LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cells†
Abstract
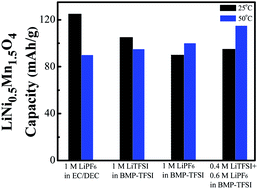
A high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material with a cubic spinel structure is synthesized using a citric-acid-assisted sol–gel process. Butylmethylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (BMP-TFSI)-based ionic liquids (ILs) with various kinds of Li salts, namely LiTFSI, LiPF6, and their mixtures, are used as electrolytes for Li/LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cells. The IL electrolytes show high thermal stability (>400 °C) and non-flammability, and are thus ideal for high-safety applications. At 25 °C, LiTFSI is more suitable than LiPF6 as an IL electrolyte in terms of cell capacity, rate capability, and cyclic stability. The IL electrolytes clearly outperform the conventional organic electrolytes at 50 °C, since the latter decomposes at high voltage and corrodes both the Al current collector and LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4, degrading the electrode performance. At such an elevated temperature, using LiPF6 to partially substitute LiTFSI in the IL electrolyte can effectively suppress Al pitting corrosion and thus improves the cell performance. In the 0.4 M LiTFSI/0.6 M LiPF6 mixed-salt IL electrolyte, an LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 discharge capacity of 115 mA h g−1 (at 0.1 C) is obtained at 50 °C with a high cell voltage of ∼4.7 V.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...