Electric field assisted chemical vapour deposition – a new method for the preparation of highly porous supercapacitor electrodes
Abstract
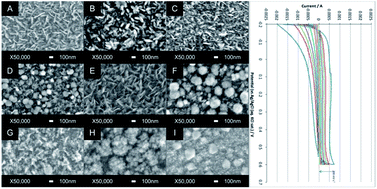
Nanostructured thin films of vanadium oxides were deposited using electric field assisted chemical vapour deposition. The films were characterised using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the films had open and porous morphologies with extremely small (5 nm) surface features. The films were made into supercapacitor cells and tested using cyclic voltammetry. It was found that stable asymptotic values specific capacitance values as high as 3700 μF cm−2 could be obtained with good cycling behaviour. Electrodes synthesized in this way show promise for applications in fields such as supercapacitors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...