Ionic conductivity enhancement of sputtered gold nanoparticle-in-ionic liquid electrolytes†
Abstract
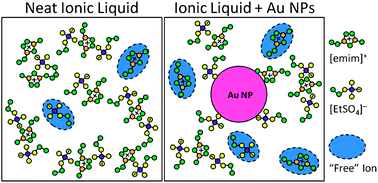
Ionic liquids (ILs) are being widely investigated as advanced electrolytes within electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) due to their inherent ionic conductivity, wide electrochemical windows, essentially zero volatility, and high temperature stability. Despite being composed entirely of ions, the ionic conductivity of a typical IL is significantly hindered by its high viscosity, rendering it akin to normal electrolytes. In this light, in order to increase the applicability of IL electrolytes, it is of the utmost priority to discover approaches for improving the electrochemical properties of ILs without adversely affecting their other beneficial attributes. In this work, we make important strides toward this goal by employing low energy sputtering to generate novel electrolytes comprising gold nanoparticle dispersions within the prototypical IL 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate, [emim][EtSO4]. This study also afforded the unique opportunity to investigate nanoscale growth mechanisms occurring within the IL. Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analyses revealed that when the IL contained a substantial fraction of sub-nanometer-sized particles, the double-layer capacitance was increased by ∼190%, concomitant with a bulk electrolyte resistance decrease of ∼70% with respect to a gold-free control. An exponential rise in resistance accompanied by a proportional decrease in capacitance accompanies nanoparticle growth until a critical size is reached—typically within 10 h at room temperature—beyond which the final capacitance is typically ∼60% higher than the control with an electrolyte resistance similar to the control. Overall, our results reveal an anomalous capacitance increase and low internal resistance for nanoparticle-in-IL dispersions, suggesting intriguing potential as electrolytes for next-generation EDLCs, fuel cells, and sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...