Unusual size-dependence of effective interactions between collapsed polymers in crowded environments
Abstract
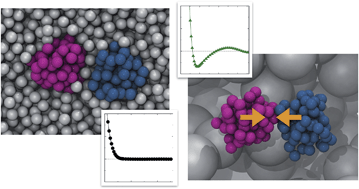
We investigate the influence of macromolecular crowding on interactions between collapsed polymers using computer simulations, to gain insights into biomacromolecular interactions in crowded biological environments. The effective attraction is induced between two collapsed polymers due to the macromolecular crowding, and it is found that the strength of the effective attraction decreases as the crowder size is reduced for a fixed crowder volume fraction, which is sharply contrasted with the conventional viewpoint based on the depletion attraction observed for hard-core spherical colloids. This unusual trend of size-dependence is interpreted by dividing the effective interaction into the polymer-mediated repulsion and crowder-mediated attraction. It is found that the ranges of repulsive and attractive contributions overlap significantly due to the flexible nature of polymer boundaries, resulting in partial cancellation over this range which leads to the observed size-dependence. Thus, this work suggests that the effective interactions between biomacromolecules in crowded environments may be qualitatively different from the depletion interactions predicted for hard-core spherical colloids.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...