Bile acid–surfactant interactions at the liquid crystal/aqueous interface
Abstract
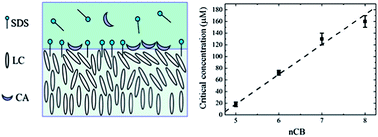
The interaction between bile acids and surfactants at interfaces plays an important role in fat digestion. In this paper, we study the competitive adsorption of cholic acid (CA) at the sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-laden liquid crystal (LC)/aqueous interface formed with cyanobiphenyl (nCB, n = 5–8) and the mixture of 5CB with 4-(4-pentylcyclohexyl)benzonitrile (5PCH). We find that the critical concentration of CA required to displace SDS from the interface linearly decreases from 160 μM to 16 μM by reducing the alkyl chain length of nCB from n = 8 to n = 5 and from 16 μM to 1.5 μM by increasing the 5PCH concentration from 0 wt% to 19 wt% in the 5PCH–5CB binary mixture. Our results clearly demonstrate that the sensitivity of 5PCH–5CB mixtures for monitoring the interaction between CA and SDS at the LC/aqueous interface can be increased by one order of magnitude, compared to 5CB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...