A model of ideal elastomeric gels for polyelectrolyte gels
Abstract
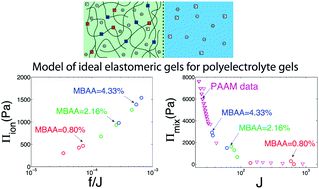
The concept of the ideal elastomeric gel is extended to polyelectrolyte gels and verified using a polyacrylamide-co-acrylic acid hydrogel as a model material system. A comparison between mixing and ion osmosis shows that the mixing osmosis is larger than the ion osmosis for small swelling ratios, while the ion osmosis dominates for large swelling ratios. We show further that the non-Gaussian chain effect becomes important in the elasticity of the polymer network at the very large swelling ratios that may occur under certain conditions of pH and salinity. We demonstrate that the Gent model captures the non-Gaussian chain effect well and that it provides a good description of the free energy associated with the stretching of the network. The model of ideal elastomeric gels fits the experimental data very well.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...