The viscosity of short polyelectrolyte solutions
Abstract
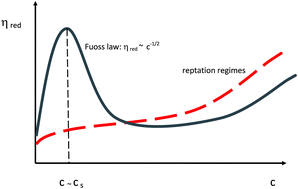
We consider the viscosity of solutions of highly charged short polyelectrolytes. Our system is a poly(styrene–maleic acid) copolymer solution (SMA) with various added salt concentrations in dilute and semidilute regimes. The SMA solutions show some particular features: (i) variations of the specific viscosity measured for different values of concentration and ionic strength can be rescaled on two universal curves when plotted as a function of the effective volume fraction; (ii) the reduced viscosity is proportional to the Debye length. In order to describe the viscosity of such a system we model the motion of the charged rods considering a simpler system: we replace each charged rod and its corresponding charge cloud by an effective neutral rod. This modified system is yet below the concentrated regime and, at most, steric interactions are left. In the semidilute regime, we model the rescaled rods moving under a mean field potential and obtain a dynamical equation for the orientational tensor, considered small, and the viscosity is derived from it. Within our mean field approach, the effects due to the rod Brownian motion and due to the potential cancel each other and the behavior of the viscosity is explained in terms of the effective volume fraction only. Our predictions are in good qualitative agreement with the experimental results over a wide range of parameters, and suggest a method for obtaining the rotational diffusion constant in the semidilute regime.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...