Freezing and phase separation of self-propelled disks†
Abstract
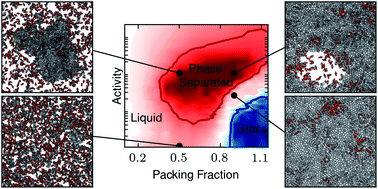
We study numerically a model of soft polydisperse and non-aligning self-propelled particles interacting through elastic repulsion, which was recently shown to exhibit active phase separation in two dimensions in the absence of any attractive interaction or breaking of the orientational symmetry. We construct a phase diagram in terms of activity and packing fraction and identify three distinct regimes: a homogeneous liquid with anomalous cluster size distribution, a phase-separated state both at high and at low density, and a frozen phase. We provide a physical interpretation of the various regimes and develop scaling arguments for the boundaries separating them.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...