Polyelectrolyte properties of filamentous biopolymers and their consequences in biological fluids
Abstract
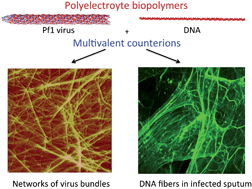
Anionic polyelectrolyte filaments are common in biological cells. DNA, RNA, the cytoskeletal filaments F-actin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments, and polysaccharides such as hyaluronan that form the pericellular matrix all have large net negative charge densities distributed over their surfaces. Several filamentous viruses with diameters and stiffnesses similar to those of cytoskeletal polymers also have similar negative charge densities. Extracellular protein filaments such collagen, fibrin and elastin, in contrast, have notably smaller charge densities and do not behave as highly charged polyelectrolytes in solution. This review summarizes data that demonstrate generic counterion-mediated effects on four structurally unrelated biopolymers of similar charge density: F-actin, vimentin, Pf1 virus, and DNA, and explores the possible biological and pathophysiological consequences of the polyelectrolyte properties of biological filaments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...