Ether solvent-induced chirality inversion of helical poly(quinoxaline-2,3-diyl)s containing l-lactic acid derived side chains†
Abstract
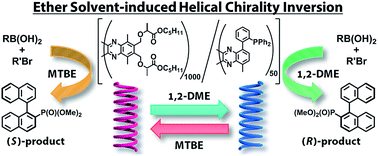
Poly(quinoxaline-2,3-diyl)s containing (S)-1-(alkoxycarbonyl)ethoxymethyl side chains derived from natural L-lactic acid were synthesized to investigate the induction of single-handed helical chirality of the main chain. In ether solvents, the handedness of the helical chirality of the polymer main chain is crucially dependent on the length of the alkyl chain in the lactate alkoxy groups. A polymer bearing pentyl ester groups showed an effective solvent-dependent helix inversion between 1,2-dimethyxyethane (1,2-DME, M-Helix) and tert-butyl methyl ether (MTBE, P-Helix). A single-handed copolymer bearing both the pentyl lactate moieties and diphenylphosphino groups was prepared to use as a chiral ligand in an asymmetric Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. The chirality of the ligand could be inverted by the choice of solvents (1,2-DME or MTBE) resulting in the production of either R- or S-enantiomers with high enantiomeric excesses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...