Highly active antibacterial ferrocenoylated or ruthenocenoylated Arg-Trp peptides can be discovered by an l-to-d substitution scan†
Abstract
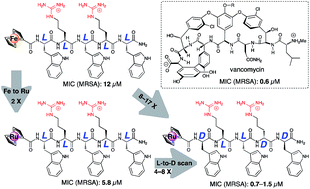
The rapid increase in resistance against common antibiotics calls for the development of novel antibiotics, particularly against multi-resistant bacteria such as the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In this work, the two group 8 metallocenoyl derivatives ferrocenoyl (FcC(O)-) or ruthenocenoyl (RcC(O)-) were attached to the N-terminus of two libraries of short antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), resulting in organometallic-AMP derivatives with as yet unparalleled antibacterial activities. In addition, these organometallic AMPs only cause limited lysis of human red blood cells (hRBCs). Our structure–activity relationship (SAR) study on these metallocenoylated peptides showed that specific combinations of L- and D-amino acid residues result in peptides with significantly improved antibacterial activity. Whereas the all-L FcC(O)-containing lead peptide had a MIC of 12 μM against MRSA, several peptides were found with MIC-values as low as 1.5–3 μM, a 4–8-fold increase in activity. For the RcC(O)-derivatized peptides a similar result was obtained: against MRSA a MIC value of 5.8 μM for the all-L peptide could be lowered to 0.7 μM, an 8-fold improvement. In addition, exposure of human red blood cells with 121 μM of the most active peptides led to a maximum hemolysis of 6%, indicating prominent selectivity that can be used to realize antibiotics based on organometallic-AMPs. We have hereby performed a systematic and highly successful SAR optimization against the two crucial parameters, i.e. antibacterial activity and hemolysis. Importantly, some of the RcC(O)-derivatized peptides presented here are among the most active antibacterial peptides; they approach or even exceed the activity of vancomycin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...