Size-dependent stability toward dissociation and ligand binding energies of phosphine ligated gold cluster ions†
Abstract
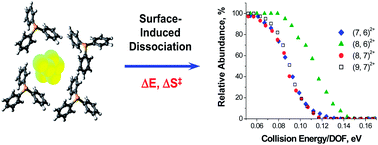
The size-dependent properties of ultra-small gold cluster ions ligated with phosphines are important to their scalable synthesis and potential applications in catalysis and energy production. However, the size distribution of clusters prepared in solution often makes it challenging to extract thermodynamic and kinetic parameters for species containing an exact number of gold atoms and phosphine ligands in a specific charge state. Here, we report for the first time the experimental determination of the stability toward fragmentation and ligand binding energies of mass-selected cationic gold clusters ligated with triphenylphosphine. Employing surface-induced dissociation Au7L62+, Au8L62+, Au8L72+ and Au9L72+ (L = triphenylphosphine) clusters are demonstrated to fragment through loss of a neutral ligand (AunLm2+ → AunL(m−1)2+ + L), asymmetric fission (AunLm2+ → Au(n−1)L(m−2)+ + AuL2+) and more symmetric fission (Au7L62+ → Au4L3+ + Au3L3+) involving charge separation of the gold core. It is shown that a cluster containing exactly eight gold atoms and six triphenylphosphine ligands, which is the predominant species formed during the early stages of reduction synthesis in solution, is exceptionally stable towards dissociation compared to the other clusters due in part to its large ligand binding energy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...