Coordination-triggered NO release from a dinitrosyl iron complex leads to anti-inflammatory activity†
Abstract
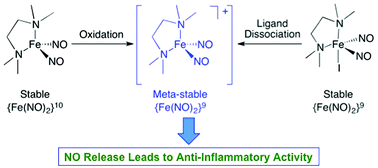
Dinitrosyl iron complexes (DNICs) are widely considered NO storage and donor molecules in cells. However, what induces an NO release from iron in DNICs and the subsequent biological consequences remain elusive. The chemistry and biology of the NO release activity of DNICs are reported here. Changes in redox status or coordination number of discrete N-bound DNICs, respectively [Fe(TMEDA)(NO)2] (1) and [Fe(TMEDA)(NO)2I] (2), can generate a metastable {Fe(NO)2}9 DNIC, [Fe(TMEDA)(NO)2]+, with νNO at 1769 and 1835 cm−1 and an EPR signal at g = 2.04, that spontaneously releases NO in solution. The NO release activity of 2 results in the up- and downregulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), respectively, in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages. Furthermore, treatment with 2 leads to downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-6, and upregulation of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the appropriate control of redox and coordination chemistry of DNICs could enable them to become anti-inflammatory agents, suggesting a potential new role for cellular DNICs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...