Electrostatics of soft charged interfaces with pH-dependent charge density: effect of consideration of appropriate hydrogen ion concentration distribution†
Abstract
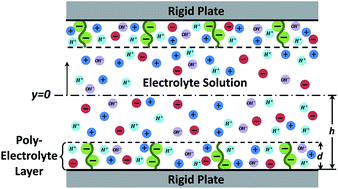
A soft charged interface, represented by a nanoscopically thick charged polyelectrolyte layer (PEL) sandwiched between a rigid solid and an electrolyte solution, forms the central element in the theoretical description of electrodynamics of soft charged biological moieties (e.g., cells, bacteria and viruses), electrohydrodynamics in soft nanochannels, and analysis of properties of non-biological gels and films. In this paper we provide a free energy based theoretical model to quantify the electrostatics of such a soft charged interface with pH-dependent charge density. Our theory considers for the first time the explicit variation of the hydrogen ion concentration inside and outside the PEL and establishes that there cannot be a uniform (within the PEL) distribution of chargeable sites within the PEL. Such uniformity causes unphysical hydrogen ion concentration jump across the PEL–electrolyte interface. In fact we demonstrate that this distribution of chargeable sites on a given polymer must obey at least a cubic variation with distance (within the PEL) in order to address this hydrogen ion concentration jump and at the same time ensure zero hydrogen ion flux at the PEL–rigid-solid interface. We anticipate that these new results will serve as a major stepping-stone towards appropriate modeling of electrodynamics and electrohydrodynamics of soft charged reactive interfaces that are paramount in the description of various micro/nanoscale biological and non-biological problems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...