Synthesis of different crystallographic Al2O3 nanomaterials from solid waste for application in dye degradation†
Abstract
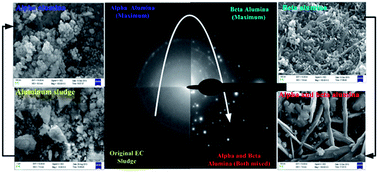
Recycling of solid wastes (sludge) generated during electrochemical (EC) treatment is one of the biggest technological challenges for scientists. Here we propose a facile approach for the preparation of active aluminium oxide nanomaterials (NMs) in different crystalline forms by recycling the sludge generated during EC treatment of textile dye wastewater. Thermogravimetric (TGA/DTA) analysis, powder X-ray diffraction (PXD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) analyses of the samples incinerated at different temperatures demonstrate formation of nanocrystalline α-, β- and γ- aluminas (Al2O3). Moreover, FE-SEM together with trans-mission electron microscopy (TEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed morphological variations of the α-, β- and γ-Al2O3 NMs but largely with uniform size and shape for respective crystallographic forms. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement indicated fairly good surface areas for the prepared Al2O3 NMs. Catalytic activity tests revealed β-Al2O3 to be most active among all other crystallographic forms reported here. The present study offers a novel and green method for the recycling of sludge (solid waste) into NMs for environmental catalysis applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...