Enhanced lithium storage capability of a dual-phase Li4Ti5O12–TiO2–carbon nanofiber anode with interfacial pseudocapacitive effect†
Abstract
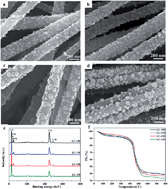
Hydrothermal treatments of electrospun titanium dioxide/carbon nanofibers (TiO2/CNFs) in LiOH solution were performed in a temperature range of 130–190 °C, and then followed by a thermal treatment at 600 °C in N2 atmosphere. The changes in morphologies, microstructures and compositions as well as the electrochemical performances with hydrothermal temperatures were investigated for all samples. The morphological and compositional characterizations showed that the surfaces of the CNFs-matrix were covered by numerous nanoparticles with size distributions of 25–100 nm. For the sample hydrothermally treated at 150 °C (denoted as LC-150), these nanoparticles (∼25 nm) were composed of well-crystalline spinel Li4Ti5O12 and anatase TiO2 with abundant phase interfaces and grain boundaries, which can induce the interfacial pseudocapacitive effect. Therefore, the as-prepared dual-phase structured Li4Ti5O12–TiO2–CNFs sample as a binder-free anode for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) presented a greatly enhanced reversible capacity (203.8 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1 after 200 cycles) and a favored rate capability (114.3 mA h g−1 at 2000 mA g−1) compared with the single-phase Li4Ti5O12–CNFs sample.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...