Ultra metal ions and pH sensing characteristics of thermoresponsive luminescent electrospun nanofibers prepared from poly(HPBO-co-NIPAAm-co-SA)†
Abstract
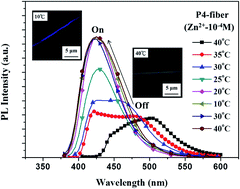
Novel multifunctional fluorescent electrospun (ES) nanofibers were prepared from random copolymers of poly{2-{2-hydroxyl-4-[5-(acryloxy)hexyloxy]phenyl}benzoxazole}-co-(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-(stearyl acrylate)} (poly(HPBO-co-NIPAAm-co-SA)) using free-radical polymerization, followed by electrospinning. The moieties of HPBO, NIPAAm, and SA were designed to exhibit zinc ion (Zn2+) and pH sensing, thermoresponsiveness, and physical cross-linking, respectively. The ES nanofibers prepared from the P4 copolymer (1 : 93 : 6 composition ratio for HPBO/NIPAAm/SA), showed ultrasensitivity to Zn2+ (as low as 10−8 M) because of the large blue-shifting of 75 nm of the emission maximum and the 2.5-fold enhancement of the emission intensity. Furthermore, the nanofibers exhibited a substantial volume (or hydrophilic–hydrophobic) change during the heating and cooling cycle between 10 °C and 40 °C, attributed to the low critical solution temperature of the thermoresponsive NIPAAm moiety. Such temperature-dependent variation of the prepared nanofibers under the presence of Zn2+ or basic conditions led to a distinct on-off switching of photoluminescence. The high surface-to-volume ratio of the prepared ES nanofibers significantly enhanced their sensitivity compared to that of thin films. These results indicated that the prepared multifunctional ES nanofibers could be potentially used in metal ion, pH, and temperature sensing devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...