Rapid determination of technetium-99 by automatic solid phase extraction and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry†
Abstract
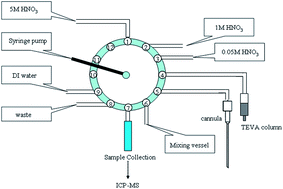
Technetium-99 (99Tc) is a key nuclide, produced by the fission of uranium-235 (235U) and plutonium-239 (239Pu), through a cascade decay process, and is one kind of target element in environmental analysis due to its long half-life (t1/2 = 2.1 × 105 years). This study developed a 99Tc analytical technique using automatic solid phase extraction (SPE) with TEVA resin and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The chemical recovery of 99Tc was 94.15 ± 3.14% and the minimum detectable activity (MDA) for cement solidified samples spiked with 99Tc was 1.5 mBq g−1 (2.4 pg mL−1). In this study, standard reference material (SRM), an environmental sample was measured by this analytical method. The proposed method is more convenient than traditional radiochemical methods in terms of reducing the time required for analysis, the consumption of reagents, and radiation exposure of operators.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...