Toxicity of ionic liquids toward microorganisms interesting to the food industry
Abstract
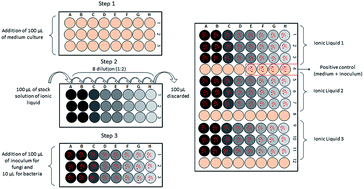
Considering the potential applications of ionic liquids (ILs) as solvents in biotechnological processes such as food production via microbial synthesis, the work presented here aimed to evaluate the toxicity of these new solvents to microorganisms of interest in the food industry. Following the international standard method of the CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute), the maximum non-toxic concentration (MNTC) was determined for nine ILs (containing an imidazolium, cholinium or phosphonium cation) toward nine microorganisms (the bacteria Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subs. delbrueckii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the actinobacteria Streptomyces drozdowiczii, the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Yarrowia lipolytica, Kluyveromyces marxianus, and the filamentous fungi Aspergillus brasiliensis and Rhizopus oryzae). Among the bacteria, B. subtilis and P. aeruginosa were more tolerant to hydrophilic imidazolium ILs with [C2mim] cations combined with [EtSO4], [EtSO3] and [Cl] anions. In the presence of hydrophilic choline and phosphonium based-ILs, the Gram-negative bacterium P. aeruginosa was more resistant than others. The same effect was observed for the [NTf2]-based ILs, in which only P. aeruginosa could grow. Regarding the fungi, A. brasiliensis and R. oryzae tolerated high concentrations of ILs. Among the yeasts, only Y. lipolytica was tolerant to all tested ILs. In general, ILs containing choline as the cationic moiety were more biocompatible since they allowed the growth of all the studied microorganisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...