Camptothecin delivery into hepatoma cell line by galactose-appended fluorescent drug delivery system†
Abstract
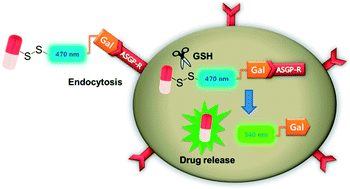
A galactose-appended camptothecin prodrug was newly synthesized. The prodrug preferentially entered a hepatoma cell line due to the galactose unit and the drug release triggered by disulfide-bond cleavage via reaction with glutathione was visualized on the basis of fluorescence changes of the naphthalimide moiety. The prodrug entered the cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis and released drug molecules into lysosomes, however, the released drug molecules failed to show significant anticancer activity, probably due to lysosomal hydrolysis of their lactone ring converting them to an inactive carboxylate form.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...