Improved microwave absorption in lightweight resin-based carbon foam by decorating with magnetic and dielectric nanoparticles†
Abstract
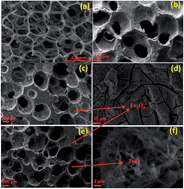
Carbon foams (CFoams) are sponge-like high performance lightweight engineering materials that possess excellent electrical and mechanical properties as well as thermal stability. CFoams possess bulk density in the range from 0.30 to 0.40 g cm−3 and open porosity of more than 70%. The CFoam consists of pore walls, i.e., ligaments, which are responsible for the conduction path and hence the electrical conductivity due to mobile charge carrier (delocalized π electron), are interconnected to each other. The high value of electrical conductivity causes the CFoam to act as an electromagnetic radiation reflector rather than an absorber; however, in certain applications, shielding materials must be able to absorb the maximum electromagnetic radiation. Therefore, to improve the absorptivity of electromagnetic radiation in lightweight CFoams, the CFoams are decorated by Fe3O4 and ZnO nanoparticles. It is observed that coating with Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–ZnO nanoparticles not only improved the absorption losses but also enhanced the compressive strength of CFoam by 100%. This modified CFoam demonstrated excellent shielding response in the frequency range from 8.2 to 12.4 GHz, in which the total shielding effectiveness (SE) was dominated by absorption losses. The total SE is −45.7 and −48.5 dB of Fe3O4 and Fe3O4–ZnO-coated CFoam, respectively, and it is governed by absorption losses of −34.3 dB and −41.5 dB, respectively. Moreover, the absorption losses increased by 236% in Fe3O4-coated CFoam and 281% in Fe3O4–ZnO-coated CFoam without much enhancement in the bulk density. This is due to the high level of magnetic and dielectric losses of nanoparticles with high surface area. Note that the absorption losses are 80% higher than any value reported for CFoam; thus, lightweight CFoam decorated with magnetic and dielectric nanoparticles is an excellent material for stealth technology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...