Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles and conducting nanobiocomposites using plant and animal sources†
Abstract
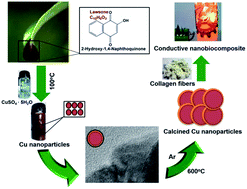
We report large-scale biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles using an extract of henna leaves as reductant. Due to the substantial electrical conductivity of the calcined copper nanoparticles, we used them to prepare conductive nanobiocomposites utilizing collagen waste. We demonstrate that the nanobiocomposites, when inserted between batteries, illuminate a light emitting diode lamp.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...