Chemical bonding in amorphous Si-coated carbon nanotubes as anodes for Li ion batteries: a XANES study†
Abstract
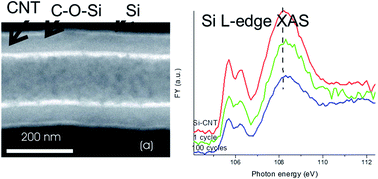
The nature of the chemical bonding in an amorphous Si-coated carbon nanotube (Si-CNT) anode, and its evolution upon electrochemical cycling, have been investigated using comprehensive X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XANES) at the Si L- and K-edges, along with the C and O K-edges. The Si nanolayer on the CNT is found to be anchored to the CNT via Si–O–C bonding. This bond weakens upon electrochemical cycling, accompanied by the generation of Li2CO3 on the surface of the Si-CNT. These findings are crucial in designing further improved Si–C composite anodes for lithium ion batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials for Energy storage

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...