Controllable synthesis of two different morphologies of Cu2O particles with the assistance of carbon dots†
Abstract
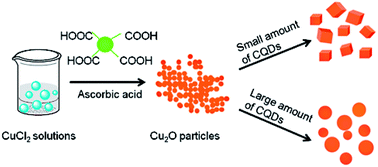
Cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanocubes and microspheres are successfully fabricated by reduction of CuCl2 upon addition of ascorbic acid as a reductive agent with the assistance of carbon dots (C-dots). The average edge length of the cubes varies from 300 to 400 nm, while the spheres fall in the range of 0.7–2 μm. The possible mechanism has been explored. By HNO3 treatment, various carbonyl functionalities are introduced to the surfaces of C-dots, thus giving rise to dramatic effects on the morphological changes of the resultant Cu2O crystals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...