Hydrogenation by nanoscale ruthenium embedded into the nanopores of K-10 clay†
Abstract
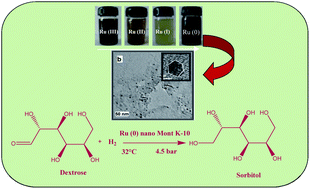
Ruthenium(0) nanoparticles in the size range 1–4 nm were generated in the nanopores of the fine fraction of Montmorillonite K-10 clay by in situ glycol reduction of RuCl3·3H2O impregnated clay. The synthesized catalyst was characterized by Powder XRD, SEM, TEM, DRS and BET surface area determination. TEM/HRTEM/SAED images revealed the growth of well dispersed Ru(0) nanoparticles having lattice fringes with interplanar spacing 0.21 nm corresponding to the [101] plane of hexagonal close packed ruthenium. The catalytic activity of the synthesized catalyst was tested for hydrogenation of cyclohexene to cyclohexane. The clay embedded Ru nanoparticles act as an efficient and recyclable environmentally friendly catalyst in hydrogenation of dextrose and phenol in aqueous medium under mild reaction conditions. Turn over frequency (TOF) of the catalyst was also calculated considering true active sites calculated on the basis of surface statistics and a model for full shell clusters.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...