Effect of Cs content on CsxH5−xPMo10V2O40 properties and oxidative catalytic activity on starch oxidation by H2O2†
Abstract
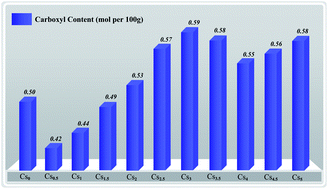
A series of cesium substituted molybovanadophosphric acids, CsxH5−xPMo10V2O40 (x = 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5 and 5.0), were synthesized by controlling the ratio of Cs+ to PMo10V2O405−. These complexes were characterized by ICP-AES, FT-IR, XRD, nitrogen physisorption, SEM and Ho measurement. The surface area and acid strength could be adjusted by changing the molar ratio of Cs to H. The highest surface areas were obtained when x = 5 and the highest acidity when x = 0. The catalytic activity of these compounds was evaluated for the oxidation of starch by H2O2, showing that the Brønsted acidity and surface area might influence the oxidation activity. Among all the prepared catalysts, Cs3H2PMo10V2O40 exhibited the best catalytic performance with a carboxylic content of 0.59 mol per 100 g, which could be attributed to the synergy of its Brønsted acidity and surface area. This solid catalyst could be reused at least 6 times without significant loss of performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...