Synergetic effect of ferrocene and MoS2 in polystyrene composites with enhanced thermal stability, flame retardant and smoke suppression properties
Abstract
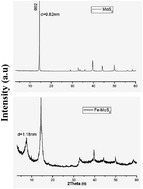
As a graphene-like layered nanomaterial, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has gained intensive attention from the materials community. In our research, MoS2 is firstly modified with ferrocene (Fe–MoS2) on a large scale and then is used as a nanofiller to prepare PS composites by a masterbatch-based melt blending method. The aim of our present study is to study the synergistic effect of ferrocene and MoS2 on the thermal stability, fire resistance and smoke suppression properties of the PS composites. It was found that the thermal stability of the PS composite was obviously enhanced upon the introduction of 3.0 wt% Fe–MoS2. The cone test results indicated that the PS/Fe–MoS2 composites exhibited superior flame retardance to PS/MoS2 and PS/ferrocene composites. Furthermore, the addition of Fe–MoS2 could improve the smoke suppression properties of PS composites, as evidenced by the reduction of the carbon monoxide production rate and smoke production rate (SPR). The total flammable gaseous products from the PS composites were decreased which further led to the inhibition of smoke. Such a significant improvement in thermal stability, fire resistance and smoke suppression properties was mainly attributed to good dispersion of the modified MoS2 nanosheets, synergistic effects between ferrocene and MoS2 nanosheets, physical barrier effects of MoS2 nanosheets and the presence of ferrocene and MoS2 can promote char formation simultaneously.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...