Electrochemical polymerization of polyaniline doped with Cu2+ as the electrode material for electrochemical supercapacitors
Abstract
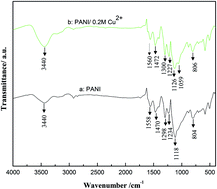
Polyaniline doped with Cu2+ (PANI/Cu2+) was synthesized by cyclic voltammetry on the stainless steel mesh with various concentrations of copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O) in an electrolyte. The structure and morphology of PANI and PANI/Cu2+ films were characterized by Fourier transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The electrochemical properties of PANI and PANI/Cu2+ films were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge–discharge testing and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in a 0.5 mol L−1 H2SO4 electrolyte in a three-electrode system. The specific capacitance of the PANI/0.2 M Cu2+ film shows a larger specific capacitance of 618 F g−1, lower resistance and better stability compared with the pure PANI film, although it is reduced to 340 F g−1 after the first 100 cycles. Thus the good capacitive performance demonstrates its potential superiority for supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...