Stable nano-sized copper and its oxide particles using cobalt tetraamino phthalocyanine as a stabilizer; application to electrochemical activity†
Abstract
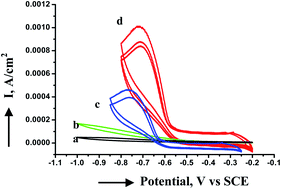
Uniform and monodisperse copper nanoparticles have been synthesized using a cobalt tetraamino phthalocyanine macrocyclic complex as a stabilizer in a one-step process in inert atmosphere. The resultant nanoparticles are characterized by electronic absorption spectra, infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The nanoparticles possess a relatively narrow size distribution. Copper nanoparticles have an average diameter of 2 to 3 nm with a spherical shape. When the copper particles are exposed to air, nanorod like structures of copper oxide nanoparticles are formed from tiny copper nanoparticles through a process involving slow oxidation of copper nanoclusters by the Ostwald ripening process and orientation attachment phenomena. In order to compare the electrochemical activity and efficiency of phthalocyanine capped copper and copper oxide nanoparticles, electrocatalytic reduction of oxygen was carried out. The copper nanoparticles showed better electrocatalytic activity than their oxide counterparts probably due to the blocking behavior of aggregated copper oxide nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...