Synthesis, structure, DNA/protein binding and in vitro cytotoxicity of new ruthenium metallates†
Abstract
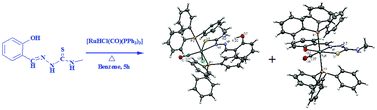
The reaction of [RuHCl(CO)(PPh3)3] with an equimolar amount of salicylaldehyde-4(N)-methylthiosemicarbazone [H2-(Sal-mtsc)] resulted in two entities, namely [Ru(H-Sal-mtsc)Cl(CO) (PPh3)2] (1) and [Ru(Sal-mtsc)(CO)(PPh3)2] (2) from a single tub. The new complexes were characterized by various spectro (IR, absorption and NMR), analytical and single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. From the crystallographic studies, it is confirmed that in complex 1, the ligand coordinated through the thiolate sulfur and the deprotonated hydrazinic nitrogen N(2), resulting in the formation of an unusual strained four membered chelate ring. The third potential donor, phenolic oxygen, remained uncoordinated. In complex 2, the ligand coordinated as an ONS chelate with the formation of more common five and six membered chelate rings. Complexes 1 and 2 have been tested for their DNA/protein binding properties by taking CT-DNA/lysozyme as models. From the protein binding studies, the alterations in the secondary structure of lysozyme by the ruthenium(II) complexes (1 and 2) were confirmed with synchronous and three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopic studies. The in vitro cytotoxicity of the newly-synthesized complexes was carried out in two different human tumour cell lines, A549 and HepG2. The cytotoxicity studies showed that complex 2 exhibited higher activity than 1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...