White light emission of multi-chromophore photoluminescent nanoparticles using polyacrylate scaffold copolymers with pendent polyfluorene groups†
Abstract
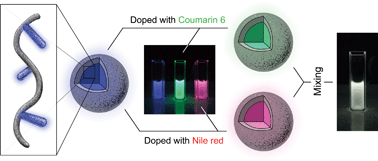
Polyfluorenes and their nanoparticles are of interest because of their desirable photoluminescent properties. Here, we report the synthesis of a polyfluorene macromonomer p-[poly(9,9-dihexylfluorene-2,7-diyl] styrene (PFS) and their narrow polydispersity PFS-containing random copolymers with t-butyl acrylate [P(PFS-r-t-BA)s], i.e. via both reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) and atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). The acid hydrolysis of P(PFS-r-t-BA) gives the corresponding amphiphilic P(PFS-r-acrylic acid) [P(PFS-r-AA)] polyelectrolytes, which self-assemble into photoluminescent nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. The P(PFS-r-AA) was shown to act as a scaffold for the incorporation of other pigments, which allowed tunable emissions via varying pigment combinations by Förster resonance energy transfer. The occurrence of strong white light emission was demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...