Tandem ATRP/Diels–Alder synthesis of polyHEMA-based hydrogels
Abstract
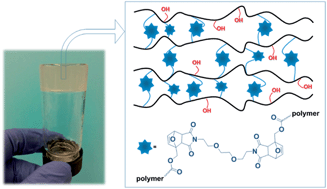
The efficient, controlled polymerization of a batch of new poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-furfuryl methacrylate)s, [poly(HEMA-co-FMA)], of various compositions was achieved using atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) in methanol. When the FMA composition did not exceed the 10 mol% ratio, the evolution of molecular weight with conversion was linear, and polydispersities were around 1.1 for polymerization reactions at 15 °C and around 1.3–1.4 at 25 °C, indicating good control over the polymerization process. HEMA-based hydrogels were obtained by means of the Diels–Alder reaction between poly(HEMA-co-FMA) and an hydrophilic bisdienophile. Gelification was monitored by diffusion-filtered 1H NMR and solution 1H NMR spectroscopy. Modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry (MTDSC) suggests the thermo-reversibility of the Diels–Alder coupling reaction of HEMA polymeric networks. Rheological studies showed that the linear viscoelasticity functions of hydrogels were influenced by the chemical composition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...