Sustainable cycloolefin polymer from pine tree oil for optoelectronics material: living cationic polymerization of β-pinene and catalytic hydrogenation of high-molecular-weight hydrogenated poly(β-pinene)
Abstract
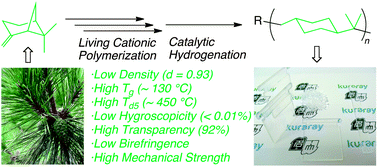
(−)-β-Pinene, a major constituent of pine tree oil, was cationically polymerized to generate a high-molecular-weight polymer and then subsequently hydrogenated via metal catalysts to give a high-performance, bio-based cycloolefin polymer with an alicyclic backbone. To obtain the high-molecular-weight polymer, the controlled/living cationic polymerization of (−)-β-pinene was investigated by an initiating system, consisting of a protonic acid, a Lewis acid, and an added base, along with an incremental monomer addition technique. Among the various systems, the RCl/EtAlCl2/Et2O system gave a high-molecular-weight poly(β-pinene) (Mw > 100 000). The catalytic hydrogenation of the obtained high-molecular-weight poly(β-pinene) was examined using various metal catalysts, among which Pd/Al2O3 enabled the quantitative hydrogenation (>99.9%) of the unsaturated C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C group in the repeating unit under mild reaction conditions (1.0 MPa pressure of H2). These reactions could be performed even at relatively large scales to produce several hundred grams of the polymer, which can be then processed through injection-molding. The synthesized bio-based cycloolefin polymers demonstrated promising potential properties as high performance optical plastics with good processability, low density, high optical transparency, low birefringence, non-hygroscopicity, high mechanical strength, and excellent thermal properties.
C group in the repeating unit under mild reaction conditions (1.0 MPa pressure of H2). These reactions could be performed even at relatively large scales to produce several hundred grams of the polymer, which can be then processed through injection-molding. The synthesized bio-based cycloolefin polymers demonstrated promising potential properties as high performance optical plastics with good processability, low density, high optical transparency, low birefringence, non-hygroscopicity, high mechanical strength, and excellent thermal properties.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Sustainable polymers: replacing polymers derived from fossil fuels

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...