Polyoxalates from biorenewable diols via Oxalate Metathesis Polymerization†
Abstract
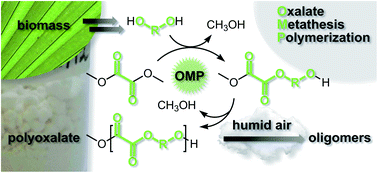
Oxalate Metathesis Polymerization (OMP) was developed for the synthesis of polyoxalates, which were subjected to molecular weight and thermal property analysis. This methodology employs para-toluene sulfonic acid for the acid-catalyzed ester interchange of dimethyl oxalate and diols. Polyalkylene oxalates were derived from dimethyl oxalate and linear diols HO–(CH2)n–OH with three to twelve methylene groups (n = 3–12). Poly(decylene oxalate), a known polymer based on (potentially biorenewable) decanediol was synthesized in 83% yield with this methodology and exhibited no discernable Tg, a Tm of 79 °C, and a Mw of 67 600 g mol−1. Polyarylene oxalates were derived from dimethyl oxalate and resorcinol bis(hydroxyethyl)ether (RBHE) or hydroquinone bis(hydroxyethyl)ether (HBHE), aromatic diols that can be obtained from biorenewable resources. The poly(resorcinol bis(hydroxyethyl)ether) oxalate (or poly(RBHE) oxalate) was obtained in 56% yield and showed a Tg of 34 °C and a Tm of 156 °C. The poly(hydroquinone bis(hydroxyethyl)ether) oxalate (or poly(HBHE) oxalate) was obtained in 88% yield and showed a Tg of 45 °C and a Tm of 190 °C. Aliphatic/aromatic polyoxalate copolymers derived from 1,10-decanediol and RBHE or HBHE in varying compositions were prepared and studied. Incorporation of the aromatic diols into the polymer chain generally afforded increased Tg and Tm. Solid-state degradation studies indicated facile water-degradation of the polyoxalates as molecular weights decreased 81–92% over the course of 13 months in humid air.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...