Versatile injectable supramolecular hydrogels containing drug loaded micelles for delivery of various drugs
Abstract
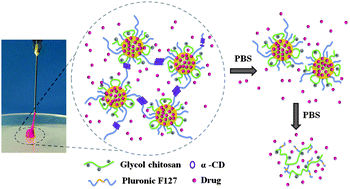
In this study, a novel glycol chitosan-Pluronic F127 conjugate (GC-PF127) was produced by adding a carboxyl group to the end of Pluronic F127 followed by an amidation reaction between carboxylated Pluronic F127 and glycol chitosan. Because of the hydrophobic aggregation of PPO segments in Pluronic F127, GC-PF127 self-assembles into micelles in aqueous solution at room temperature. The micelles can effectively load amphiphilic doxorubicin (DOX) and partly load negatively charged protein superoxide dismutase (SOD) at neutral pH with different mechanisms, but cannot load hydrophilic 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). The respective DOX/GC-PF127, SOD/GC-PF127, and 5-FU/GC-PF127 micelle solutions can be converted to injectable supramolecular hydrogels by addition of α-CD. The strength and dissociation rate of the hydrogels can be tuned by the α-CD concentration. The hydrogel structure can recover immediately after extrusion of the hydrogel using a syringe. The hydrogels have prolonged and almost linear release behaviours for various drugs. The hydrogels release free drugs as well as drug loaded micelles via the dissociation of the hydrogels under physiological conditions, which may enhance the targeting ability and therapeutic efficiency. The released micelles sequentially release free drugs that further prolong the release of the drugs. GC-PF127 hydrogels are versatile injectable hydrogels which can deliver various drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...