Covalent and non-covalent approaches to suppress plasticization of polymer membranes for gas separation
Abstract
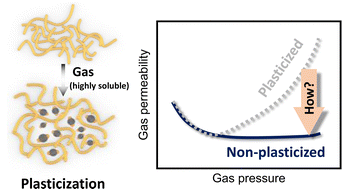
Polymer membranes represent an attractive platform for energy-efficient gas separation, but they are known to suffer from plasticization during continuous gas-separation processes. This phenomenon is caused by the spontaneous relaxation of individual polymer chains arising from the swelling effect induced by high-pressure highly soluble gases such as CO2, and it weakens the stability of the membrane, leading to a significant loss of selectivity during the separation of mixed gases. Thus, minimizing the disadvantages of polymer membranes is essential to ensure reliable gas-separation performance for practical applications. This feature article summarizes the theory underlying the plasticization of polymer membranes and introduces covalent and non-covalent approaches to suppress plasticization behaviour on a molecular level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...