Investigation of desilylation in the recognition mechanism to fluoride by a 1,8-naphthalimide derivative†
Abstract
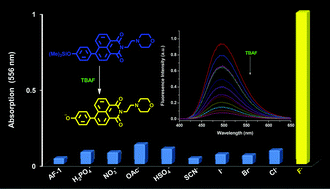
A reaction-based chemosensor (AF-1) was designed, synthesized and applied as an optical approach for quantitative measurement of F− in MeCN. In the presence of F−, selective fluoride-assisted desilylation instantly gave colorimetric and fluorogenic signals, providing a dual-optical channel for the detection of F−. 1H NMR titration was carried out to investigate the desilylation process, revealing F− triggered rapid cleavage of Si–O bond in trimethylsilyl ether. AF-1 exhibited high sensitivity and selectivity to F− over other anions. The detection limit to F− was calculated to be 0.05 ppm.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...