A hydrophobic disordered peptide spontaneously anchors a covalently bound RNA hairpin to giant lipidic vesicles†
Abstract
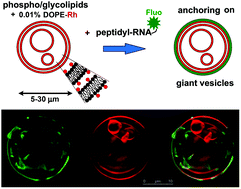
The attraction of nucleic acids to lipidic compartments is the first step for carriers of potentially inheritable information to self-organise in functionalised synthetic cells. Confocal fluorescence imaging shows that a synthetic amphiphilic peptidyl RNA molecule spontaneously accumulates at the outer bilayer membranes of phospho- and glycolipidic giant vesicles. Cooperatively attractive interactions of −3.4 to −4.0 kcal mol−1 between a random coil hydrophobic peptide and lipid membranes can thus pilot lipophobic RNA to its compartmentation. The separation of mixed lipid phases in the membranes further enhances the local concentration of anchored RNA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...