19F NMR spectroscopy monitors ligand binding to recombinantly fluorine-labelled b′x from human protein disulphide isomerase (hPDI)†
Abstract
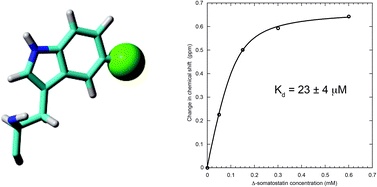
We report a protein-observe 19F NMR-based ligand titration binding study of human PDI b′x with Δ-somatostatin that also emphasises the need to optimise recombinant protein fluorination when using 5- or 6-fluoroindole. This study highlights a recombinant preference for 5-fluoroindole over 6-fluoroindole; most likely due to the influence of fluorine atomic packing within the folded protein structure. Fluorination affords a single 19F resonance probe to follow displacement of the protein x-linker as ligand is titrated and provides a dissociation constant of 23 ± 4 μM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...