Efficient synthesis of mibefradil analogues: an insight into in vitro stability†
Abstract
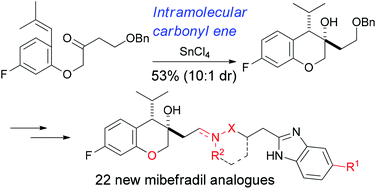
This article describes the synthesis and biological evaluation of a chemical library of mibefradil analogues to investigate the effect of structural modification on in vitro stability. The construction of the dihydrobenzopyran structure in mibefradil derivatives 2 was achieved through two efficient approaches based on a diastereoselective intermolecular Reformatsky reaction and an intramolecular carbonyl–ene cyclization. In particular, the second strategy through the intramolecular carbonyl–ene reaction led to the formation of a key intermediate 3 in a short and highly stereoselective way, which has allowed for practical and convenient preparation of analogues 2. Using this protocol, we could obtain 22 new mibefradil analogues 2, which were biologically tested for in vitro efficacies against T-type calcium channels and metabolic stabilities. Among the synthesized compounds, we found that analogue 2aa containing a dihydrobenzopyran ring and a secondary amine linker showed high % remaining activities of the tested CYP enzymes retaining the excellent T-type calcium channel blocking activity. These findings indicated that the structural modification of 1 was effective for improving in vitro stability, i.e., reducing CYP inhibition and metabolic degradation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...