Callyspongisines A–D: bromopyrrole alkaloids from an Australian marine sponge, Callyspongia sp.†
Abstract
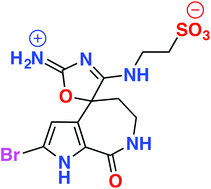
An extract of the Great Australian Bight marine sponge Callyspongia sp. (CMB-01152) displayed inhibitory activity against the neurodegenerative disease kinase targets casein kinase 1 (CK1), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3β). Chemical investigation, employing HPLC-DAD-MS single ion extraction protocols, facilitated identification of the new bromopyrrole alkaloids, callyspongisines A–D (1–4), and two known co-metabolites, hymenialdisine (5) and 2-bromoaldisine (6). Structure elucidation of 1–6 was supported by detailed spectroscopic analysis and chemical interconversion, as well as biosynthetic and synthetic considerations. Callyspongisine A (1) is only the second reported example of a natural imino-oxazoline, and the first to feature a spiro heterocyclic framework, while callyspongisines B–D (2–4) were speculated to be storage and handling artefacts of 1. The kinase inhibitory activity detected in Callyspongia sp. (CMB-01152) was attributed to 5.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...